Menopause brings numerous changes, and itching might not be the first symptom that comes to mind. Yet, for many women, persistent and sometimes seemingly unexplained itching can become a noticeable part of the menopause journey. Understanding why this occurs and how to manage it can help provide relief and restore comfort.
When does itching start during menopause?
Itching related to menopause can emerge during perimenopause, sometimes as early as in the late 30s. This symptom often intensifies as menopause approaches and hormone levels fluctuate more dramatically.
Low estrogen levels, common in perimenopause and menopause, reduce the skin’s natural moisture and thin its protective layers. This makes the skin more sensitive and prone to dryness and irritation, increasing the likelihood of itching. While some experience occasional mild irritation, others may notice more intense itching sensations, like tingling or burning, that can disrupt sleep and daily activities.(1)(2)
Causes of Itching During Menopause
Several factors contribute to itching during menopause:(1)(2)(3)(5)(6)
Hormonal Fluctuations: Estrogen levels decline, leading to thinner, drier skin and increased sensitivity.
Dry Skin and Collagen Loss: Reduced collagen production exacerbates dryness, making the skin less elastic and more prone to irritation.
Histamine Release: Hormonal changes can increase histamine sensitivity, amplifying itching.
Body Temperature Changes: Hot flashes and night sweats elevate skin moisture, which can evaporate quickly, causing dryness and discomfort.
Stress and Anxiety: Heightened stress levels during menopause can weaken skin health, further aggravating itching.
Skin Barrier Function and pH Changes
During menopause, the function of the skin's barrier can become compromised. Estrogen is critical in maintaining skin health by supporting hydration, elasticity, and collagen production. Its decline during menopause leads to increased transepidermal water loss and a reduction in dermal collagen, contributing to dryness and heightened sensitivity. Additionally, skin pH may become more alkaline, further contributing to irritation and itching. Maintaining skin hydration and using pH-balanced skincare products can help mitigate these effects.(1)(3)(7)
Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms
Menopause is associated with a decline in the skin's natural antioxidant defenses, making it more susceptible to oxidative stress and environmental damage. Incorporating antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, into a skincare routine or diet may support skin health during this time.(1)
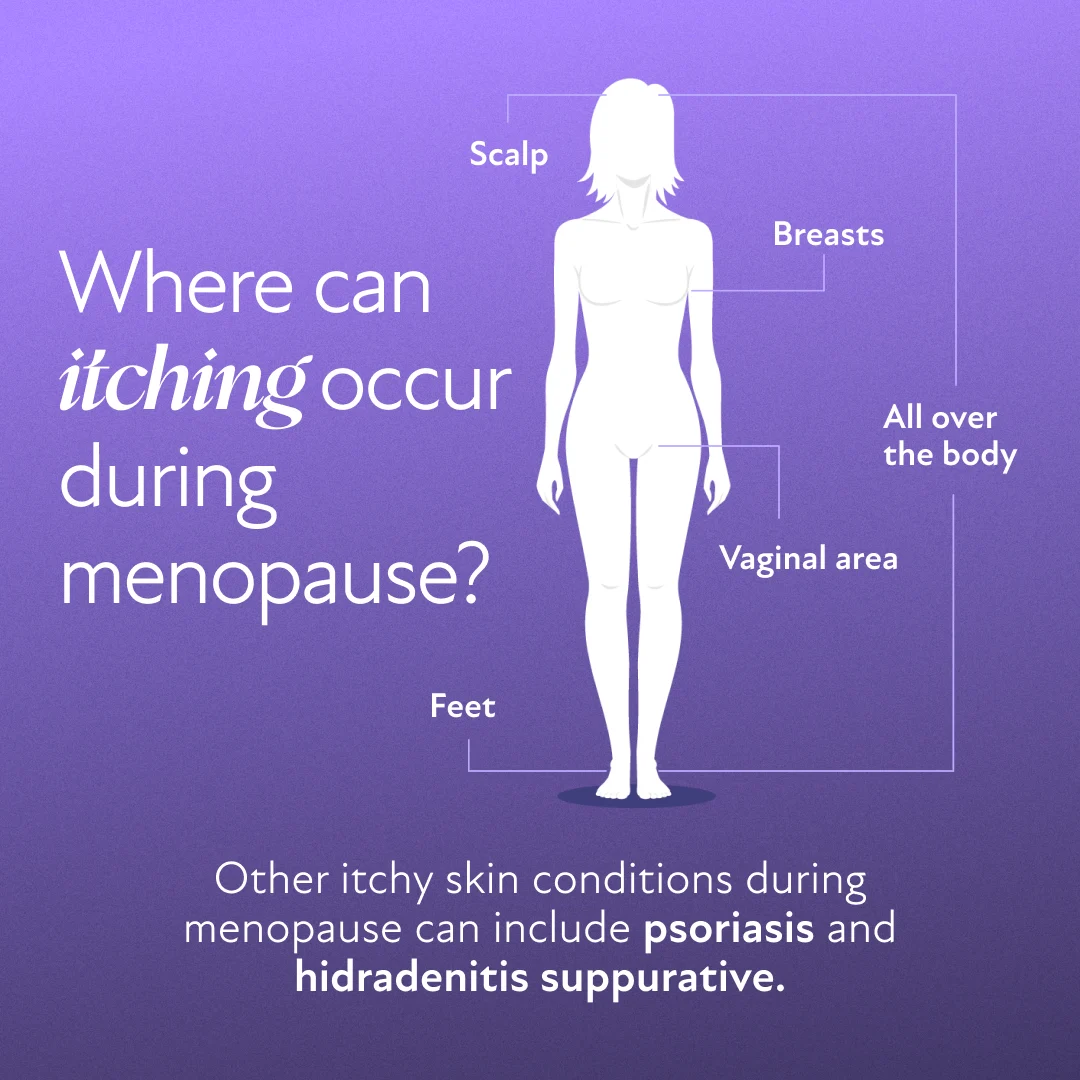
Areas Affected by Itching During Menopause
Itching can occur in specific areas or affect the body more generally. Each location often has unique underlying causes and solutions.
Itchy Skin All Over the Body
Generalized itching stems from skin dehydration and reduced natural oils. Environmental factors, such as dry indoor air or exposure to cold weather, can worsen the condition. Commonly affected areas include the arms, legs, abdomen, and back.(1)
Itchy Scalp
Hormonal shifts can lead to a drier scalp, contributing to flakiness or conditions like dandruff. Seborrheic dermatitis, which worsens with hormonal changes, may also cause itching. Gentle hair care and moisturizing treatments can help alleviate discomfort.(1)(4)
Itchy Vaginal Area
The vulva is especially sensitive during menopause due to reduced estrogen levels, leading to vaginal dryness and pH imbalances. These changes heighten the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) or yeast infections, which can intensify itching.(7)
Itchy Feet
Itchy feet may result from nerve sensitivity or circulation changes linked to menopause. Wearing tight or non-breathable footwear can aggravate this issue. Proper foot hygiene and moisturizing creams are simple yet effective solutions.(9)
Itchy Breasts
Hot flashes and sweating can cause moisture buildup under and between the breasts, leading to irritation. Wearing the wrong bra size or synthetic fabrics may exacerbate itchiness. Choosing a properly fitted bra made from breathable materials can provide relief.
Psoriasis and Menopause
Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition causing scaly, inflamed patches on the skin, may be impacted by menopause. Hormonal fluctuations during this period could exacerbate psoriasis symptoms or trigger new onset. Managing stress, staying hydrated, and working with a dermatologist are crucial for effective treatment.(3)
Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition that primarily involves sweat glands within the dermis. It’s characterized by painful lumps under the skin, particularly in areas where the skin rubs together, such as under the breasts, armpits, or groin. While not exclusively caused by menopause, hormonal changes during this phase may influence its development or progression. Early treatment is essential to manage symptoms and prevent complications.(3)
How to Relieve Itching During Menopause
Relief from menopausal itching may involve a combination of natural remedies and medical treatments. Gentle skincare routines and the use of products designed for sensitive skin can be beneficial for individuals experiencing menopausal itching.
Natural Remedies for Itching During Menopause
Herbal Remedies: Chamomile, peppermint, and lavender have calming properties that may soothe irritated skin.
Dietary Adjustments: Drinking lots of water and incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fish and flaxseeds, can improve skin hydration. Staying well-hydrated supports overall skin health.
Topical Treatments: Aloe vera, coconut oil, oat balm, and some herbal oils may reduce irritation and redness.
Hydration and Moisturizing: Using non-comedogenic, fragrance-free moisturizers immediately after bathing helps retain skin moisture.(10)
Avoiding Irritants: Harsh or scent-heavy soaps, extra hot showers, tight clothing, and synthetic fabrics can worsen skin dryness and irritation. Opting for gentle cleansers and breathable clothing made from natural fibers can help provide relief.(10)
Medical Treatments for Itching During Menopause
Over-the-Counter Options: Antihistamines or corticosteroid creams may alleviate severe itching, but it’s crucial to evaluate options with a doctor first.(10)(11)
Topical Treatments for Vulvar Itching: Vaginal moisturizers or topical estrogen can address itching in sensitive areas.(7)
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Balancing hormones with HRT can significantly reduce skin dryness and itching.(1)(7)(8)
When to See a Doctor for Itching During Menopause
While many itching symptoms resolve with home treatments, certain signs require medical attention. A healthcare provider should evaluate persistent or worsening itching, rashes, redness, or swelling. Vulvar itching accompanied by pain or unusual discharge warrants immediate consultation with a gynecologist.
Is hormone replacement therapy (HRT) effective for itching during menopause?
HRT helps address hormonal imbalances, which are a primary cause of menopausal itching. By restoring estrogen levels, HRT can help improve skin hydration and elasticity. Localized estrogen treatments, such as creams, specifically target vaginal and vulvar itching, providing effective relief.(1)(3)(8)
Addressing Menopausal Itching
Menopause-related itching can be disruptive but is often manageable with the right approach. Understanding the hormonal and environmental factors behind the discomfort allows for targeted treatment. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, natural remedies, or medical interventions, relief is within reach.
Struggling with itching during menopause? Discover if HRT is right for you.
If you’ve entered the menopause transition and are dealing with constant itching, you’re not alone. Take Winona’s menopause quiz to see if you’re an eligible candidate for HRT. Get started with Winona to take the first step toward feeling better.